
A Guest Post by ObstacleChick
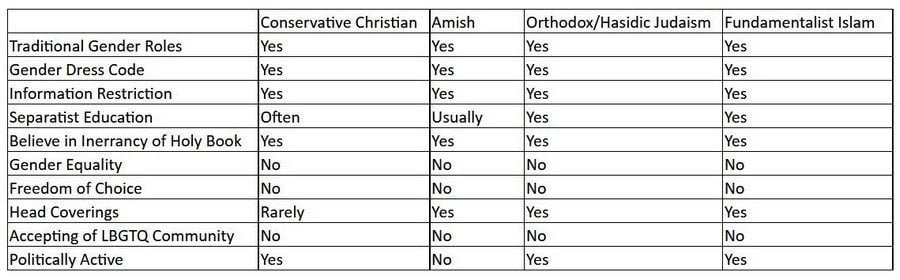
What is religious fundamentalism? Typically, it is an unwavering and unapologetic belief in the absolute authority of a religious text or texts. Adherents believe their religion is the one true religion and that its precepts should govern all aspects of life. The ultimate goal is the governance of everyone’s lives under the rules and standards of the religion’s holy book(s). Rules are comprehensive, encompassing behavior, dress, gender roles, and access to information, media, and technology. Adherents believe that their religious beliefs and practices should be exempt from criticism, and any form of criticism is labeled as heresy or persecution. There are many types of religious fundamentalists throughout the world, but here in the United States we are most familiar with fundamentalist evangelical Christians, fundamentalist Muslims, orthodox and Hasidic Jews, and Old Order Amish (which are fundamentalist in their adherence to their religious text, but not with regard to forcing their beliefs on those outside their community).
As disparate as these groups may seem on the surface, they have much in common. Each group believes that its holy text is an absolute, inerrant authority for all aspects of life. It is not uncommon for these groups to separate themselves from their surrounding communities, focusing almost exclusively on staying within their religious communities with regard to their worship activities, leisure activities, and even employment. Orthodox and Hasidic Jews, for example, must be work for an employer that is flexible with regard to Jewish holy days and for leaving work early on Fridays for Shabbas. Not in all cases, but frequently children are sent to sect-approved/operated schools. In Amish communities, education is forbidden past 8th grade, and in communities that have their own schools, the teachers are young women within the community who have no education past 8th grade. For Hasidic Jews, girls and boys attend gender-segregated schools. Boys attend yeshivas where the focus of education is on studying the Talmud. Little attention is given to other subjects, and evolution is not taught. Among Evangelicals, it is popular to either home school one’s children or to send them to a fundamentalist Christian school, where, again, evolution is not taught to children. Fundamentalist Muslims often send their children to madrasas where the focus is on religious education. In some Muslim-controlled countries, girls are not educated.
Fundamentalists of all stripes give great authority to religious leaders who often dictate the rules of each separatist community. In Amish communities, there is a bishop, two or three ministers, and a deacon. Each must be nominated, but lots (similar to drawing straws) are drawn to determine which man receives which position. The leaders are responsible for the spiritual education of their congregation as well as making sure the Ordnung — the set of rules specific to each community — is followed. Each church district’s leaders set specific rules for its community, which is why there can be slight differences from one Amish community to another. In Evangelical sects and churches, great authority is given to pastors. Bruce has spoken about this a number of times, so there’s no need for me to expound on the matter here. In Orthodox or Hasidic communities, the rebbe is the authority, and he sets the rules specific to that local community. Rules may include color of stockings women are required to wear or what books are allowed in the Hasidic libraries. In fundamentalist Muslim communities, the imam is the ultimate authority, and he may issue fatwas or rules specific to his community. (Please note that all leaders are male.)
In each of these fundamentalist religions, gender roles are specifically defined in traditional ways. Men are considered to be the leaders of the family, the breadwinners, the final authorities in the household; the ones who commune most closely with their deity. Women are considered to be the nurturers, the caretakers of children, submissive to the authority of their husbands. Typically, women are not allowed to work outside the home in many fundamentalist sects/churches. Amish women are, however, permitted to sell their goods at markets or operate roadside stands for home-grown and home-baked goods. Women are not allowed any positions of leadership beyond teaching women or young children. Marriage is considered to be between one man and one woman, and these communities are not known for acceptance of LBGTQ people.
Dress codes are important among these communities. The Amish are easily identified as their clothing styles have not changed in centuries. They are referred to as “Plain People” because their styles are simple, solid colors typically limited to black, brown, burgundy, blue, purple or green (though some communities may allow other colors). Women wear dresses and aprons secured with straight pins (no buttons, which are considered vain), and they wear a white kappe (head covering) so they may pray at any time. Men wear dark suits with hook & eye closures (no buttons and no fancy belt buckles), suspenders, and a black or straw hat.
For fundamentalist Christians, there is often no exact standard of dress other than “modesty” for women, though many fundamentalist Baptist churches have complex, exacting dress codes. Many fundamentalist Christian women wear skirts or dresses at least knee length, no low-cut tops, and they typically wear sleeves. Women will be shamed for showing too much skin or wearing something too tight.
Hasidic communities have strict hair and clothing rules as well. Married women must keep their hair short and wear a sheitel wig; women wear dresses or skirts; their sleeves must be at least three-quarter length; they must wear thick, opaque stockings (often black, occasionally flesh colored though that is forbidden in some communities); and a lot of black, loose clothing, though blouses or sweaters may be colorful. Married men must sport a beard and side curls (payot) which they can never cut. Most men wear a white button-down shirt and black pants and jacket. A yarmulke must be worn at all times, and when praying, men wear a tallit, or prayer shawl, with tzitzit, or fringe, to remind them of God’s commandments.
Fundamentalist Muslim women must be covered in mixed company, and the culture determines how much covering is required. The most extreme version is the burqa with the niqab (face covering). Men may wear a taqiyah or cap when praying.
Each of these fundamentalist religions believes secularism is the greatest threat to their sect, churches, and beliefs. Access to secular libraries or media may be prohibited, restricted, or discouraged. Often, only books approved by church leaders are permitted to be read. The Amish prohibit technology altogether, though they are allowed to check out elder-approved books at public libraries. Fundamentalist Christians are generally admonished to limit their media access to “G-rated” or Christian-published format. Many Hasidic communities forbid access to secular libraries. In fundamentalist Muslim-controlled countries, all media are controlled by the religious leaders, thus preventing people from accessing any non-approved content. Each of these groups limits media access for “moral” reasons, but they also want to prevent community members from accessing any knowledge that may contradict their sect’s teachings.
While some of Amish people vote, they do not seek public office, and their pacifism prevents them from joining the military. They also are not visibly active in campaigning. Myriads of articles have been written — particularly before and after the 2016 presidential election — concerning the political activism of evangelical Christians. Orthodox and Hasidic Jews are known for their political activism for candidates sympathetic to their communities, particularly as it is an “honor” for Jewish men to collect welfare and food stamps so they can exclusively focus their time on Talmudic studies. As far as fundamentalist Islam is concerned, there are many countries in which fundamentalist Islam controls government.
In Bruce’s recent post Life After Jesus: Moving from a God-Shaped Hole to a Knowledge-Shaped Hole he talks about restrictions that fundamentalist Christian authorities put on secular influences. Indeed, venturing beyond fundamentalist-bubble-approved media is considered a temptation by Satan and demonic forces, potentially leading someone to everlasting torment in hell. Pastors try to scare their flocks into not watching the latest season of “Cosmos” or “Game of Thrones”; that rock music leads to the “Highway to Hell”; that evolution is Satan’s greatest deception. Amish and Hasidic communities threaten members with excommunication if they do not adhere to community standards. For the skeptical or curious in these communities, fear of being cut off from family and friends is a real concern. In addition, many members (particularly women) are poorly educated and lack job skills, so escaping these communities is, at best, a risky venture. Mission to Amish People (MAP) and Charity Christian Fellowship are organizations that help Amish people leave their communities, and Footsteps is an organization that helps Hasidic Jews leave theirs. Organizations such as these offer practical and emotional support to deconverts. Those of us in the real world realize that knowledge is power, and fundamentalists do their best to limit knowledge, thus limiting the power of their flocks.
 I look at all these groups and think, there’s no way I could live in one of those communities. After I graduated from high school, I did my best to escape the clutches of fundamentalist Christianity. Fortunately, I possessed a college degree from a highly ranked secular university and developed marketable skills, so I was able to support myself financially. Many in these communities, particularly women, are purposely raised without these skills, ensuring reliance on the community. It is my firm conviction that any group that purposefully restricts access to knowledge and education and discourages contact with outsiders is inherently harmful and potentially abusive. Those in power may thrive within these systems, but the systems themselves are designed to benefit those in power at the expense of the powerless.
I look at all these groups and think, there’s no way I could live in one of those communities. After I graduated from high school, I did my best to escape the clutches of fundamentalist Christianity. Fortunately, I possessed a college degree from a highly ranked secular university and developed marketable skills, so I was able to support myself financially. Many in these communities, particularly women, are purposely raised without these skills, ensuring reliance on the community. It is my firm conviction that any group that purposefully restricts access to knowledge and education and discourages contact with outsiders is inherently harmful and potentially abusive. Those in power may thrive within these systems, but the systems themselves are designed to benefit those in power at the expense of the powerless.
(If you are interested in finding out more about the Old Order Amish, I recommend the book Amish Society by John A. Hostetler for a comprehensive examination. For those who have access to Netflix and are interested in deconverts from Hasidic Judaism, I recommend the documentary One of Us regarding the Hasidic community in Brooklyn and in Rockland County, New York. Both are communities with which I am familiar as I live in proximity to both).
Now, for a bit of levity: Amish Paradise by Weird Al Yankovic
