Julia Harte, writing for The Center For Public Integrity, had this to say about the US Military’s 2015 budget:
The U.S. military’s budget request now pending on Capitol Hill includes a particularly notable oddity inside the special fund meant to support combat operations in Iraq and Afghanistan: a new $810 million U.S. defense initiative to “reassure” Europeans of their security in the wake of Vladimir Putin’s Crimean land grab.
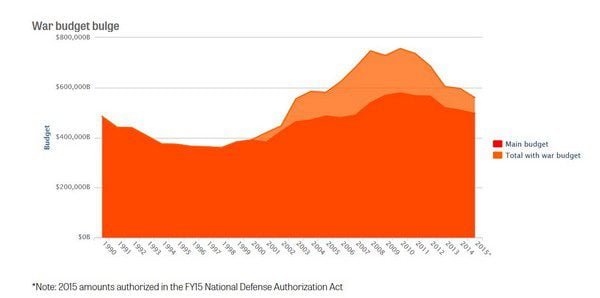
This is not how America’s war budget – otherwise known as the Overseas Contingency Operations (OCO) fund – is supposed to work. The White House in 2011 reaffirmed that the OCO, originally established in 2001 under a different name, was for “temporary and emergency requirements” associated with U.S. combat operations in Iraq and Afghanistan. Now, many experts say its continued use is emblematic of a five-year collapse in Washington’s fiscal discipline.
The OCO budget isn’t subject to spending limits that cap the rest of the defense budget for the next seven years; it’s often omitted altogether from tallies of how much the military spends each year; and as an “emergency” fund, it’s subject to much less scrutiny than other military spending requests.
This sort of special war funding was supposed to decline and then disappear as combat operations in Iraq and Afghanistan wound down. But that target has receded, if not disappeared altogether, as the OCO fund has become a larger catchall — a slush fund used by the military services, by lawmakers, and by the White House to escape budgetary constraints, officials and independent experts say.
Although President Barack Obama promised as a candidate in 2008 to “end the abuse” of wartime emergency spending, it’s now clear he will not do so before leaving office in 2016, these experts agree. This year, the main defense authorization budget is likely to come in at a cool $521.3 billion, snugly within the legal limits for federal spending in 2015. But the OCO includes an additional $63 billion. As a result, more than a tenth of all Pentagon spending will remain uncapped and subject to much less scrutiny than the remainder.
The European initiative is just one of many programs in the OCO budget that have little or nothing to do with the Iraq and Afghanistan wars. The new Defense Authorization Act for 2015, which may be signed by the president in coming days, includes $55 million to retain the “air superiority presence” of the U.S. Air Force. Another $351 million of OCO funds would go to Israel for its Iron Dome missile defense system….
…Moreover, the OCO budget isn’t a fiscal salve only once a year. The Defense Department comptroller can — and often does — ask the House and Senate committees on appropriations and armed services for permission throughout the year to add new spending to the OCO budget if programs already in that budget wind up costing less than anticipated. Often, additional non-emergency expenses sneak in during that process.
Over the past four years, for example, the Defense Department’s comptroller has sought congressional approval to add roughly $20 billion worth of expenditures to OCO to cover costs not previously stated in the budget, including many that do not appear to be emergencies or directly related to combat operations, according to a CPI tally.
These “reprogrammings” are typically approved without a public hearing, based merely on written assent from the four chairmen of Congress’s defense-related committees. Their letters are rarely made public.
On occasion, however, the Pentagon submits a reprogramming request for OCO funding so outlandish that lawmakers reject it publicly. That’s what happened on September 8, when Comptroller Michael McCord requested $1.5 billion in OCO funds to purchase 21 Apache helicopters, eight F-35 Joint Strike Fighter planes, and assorted spares and repair parts to replace aircraft that the U.S. Army, Navy, and Air Force had lost in battles over the past two years…
…A close examination of OCO reprogramming requests that sailed through over the past three years reveals many that seem unrelated to core Iraq and Afghanistan emergency fighting needs: an $86 million request for unemployment compensation for ex-servicemembers; a $13.7 million request for funds to help prosecute alleged 9/11 conspirators; and a $104.5 million request to help test a bomb capable of destroying bunkers 200 feet underground…
…Far from the original OCO task of providing direct support for combat operations in Iraq and Afghanistan, the administration’s current OCO mandate anoints the Pentagon a global therapist, bodyguard, and trainer — and gives it uncapped funding to do all that those roles entail.
You can read the entire report here.
