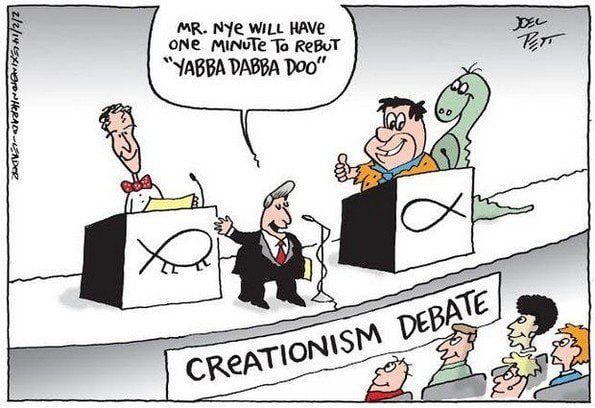
Troy Lacey, a writer for Answers in Genesis, recently wrote an article titled Answering Atheists. Lame from start to finish, Lacey tries to deconstruct quotes from Bill Nye, Neil deGrasse Tyson, and Richard Dawkins. (These men, by the way, are not top-shelf atheists. Lacey might want to engage atheists who are schooled in Christian theology and dogma.)
With the Bible as our starting point, we can look at the natural laws that God created, such as laws of thermodynamics and the law of biogenesis, and we can examine whether natural selection and mutation could possibly account for molecules-to-man evolution. They can’t. Instead, they clearly show the Creator (Romans 1:18–20).
Far from refusing to look at any evidence, creationists carefully examine it all. Creationist articles, books, and museums regularly cite the specific evolutionary arguments and then test them using the most rigorous scientific and philosophical tools available. We desperately want to know the truth so we can speak accurately about the Creator and his handiwork. We have no fears where the evidence will lead because we know it all points to God’s glory.
Oh, the lies young earth creationists tell. Do creationists really “carefully examine it [evidence] all?” Do they “desperately want to know the truth?” Of course not. Most young earth creationists are presuppositionalists. Creationists don’t start with evidence, they start with the following presuppositions:
- The Protestant Bible is the inspired, inerrant, and infallible Word of God
- The one True God is the triune God of the Bible
- God created the earth in six literal twenty-four-hour days, 6,028 years ago
- God destroyed the human race, save eight people, with a worldwide flood
I could add more Evangelical presuppositions, but these will suffice for now. Instead of weighing the evidence for these claims, they presuppose that they are true. Granted, none of us is free of presuppositions, We should do everything we can to limit our presuppositions. Evangelicals, on the other hand, have presuppositions upon presuppositions. These presuppositions keep them from seeing, knowing, and understanding the truth. And it is for this reason that it is nearly impossible to argue/debate Evangelical apologists. Presuppositions are faith claims that are impervious to falsification. Either you believe them to be true, or you don’t.
Lacey lives in a bubble where he genuinely believes that creationists are “using the most rigorous scientific and philosophical tools available.” He says that creationists do not “fear where the evidence will lead.” Why? Here comes another presupposition: we know it all [all evidence] points to God’s glory. Does all evidence point to God’s glory? Of course not. This is a faith claim.
Long before we can discuss “creationism,” we must first debate the claims Evangelicals make for the existence of God and the supernatural nature of the Bible. Lacey wants atheists to take his word for these claims. Not going to happen. Most atheists are rationalists and skeptics. We expect Evangelical apologists to provide some sort of evidence for their claims. Lacey claims Evangelicals like him examine and test every claim made by scientists. Is this a true claim? If yes, then why are so few creationist scientists published in scientific journals; not creationist or Evangelical journals, but well-respected science journals? Cue claims of persecution or bias. That’s how Evangelicals explain their overwhelming lack of publication in non-sectarian science journals. “The evil evolutionists are out to get us,” Evangelicals claim. However, the more likely explanation is that their claims lack scientific standing, and no reputable journal is going to give space for nonsense to be published.
Bruce Gerencser, 68, lives in rural Northwest Ohio with his wife of 47 years. He and his wife have six grown children and sixteen grandchildren. Bruce pastored Evangelical churches for twenty-five years in Ohio, Texas, and Michigan. Bruce left the ministry in 2005, and in 2008 he left Christianity. Bruce is now a humanist and an atheist.
Your comments are welcome and appreciated. All first-time comments are moderated. Please read the commenting rules before commenting.
You can email Bruce via the Contact Form.